What is ETFs Trading [1]
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment funds that are traded on stock exchanges, much like individual stocks. They’re designed to track the performance of a specific index, sector, commodity, or asset class. ETFs offer traders a way to access diversified assets without having to trade each individual security separately.
If you are new to ETFs trading, learn more about ETF Trading for beginners in the Vantage Academy.
Trade ETFs using CFDs
An alternative method to trade the price fluctuations in ETFs is through the use of Contracts For Differences (CFDs).
When you trade CFDs, you enter into a contract with the broker you trade with, speculating on the rise or fall in the future price of the underlying asset. Trading CFDs allow you to go both long or short and provide the opportunity to capitalise on price movements without having to own the actual asset.
It’s important to learn about the underlying ETF you are trading for and understand what’s happening in the markets. When trading CFDs with leverage, you should also only trade with an amount you can afford to lose. To learn more about examples of ETFs CFD trading, refer to our comprehensive guide here.
5 Benefits of Trading ETFs
ETFs allow traders to trade diversified baskets of securities with a single trade and can be traded on an exchange throughout the day. While they are not a guaranteed path to success, they offer several attractive features that make them popular among traders.
Here are the 5 benefits of trading ETFs:
1. Diversification [2]
ETFs offer convenient portfolio diversification without the need for individual stock, bond or commodities selection. The purchase of an ETF allows you to diversify your portfolio in a single trade, rather than having to make individual trades of securities which would come with additional trading costs.
ETFs can contain constituents that are specific to various major asset classes and sectors, offering you a wide range of choices. For example, you can get exposure to the gold market with an ETF like SPDR Gold Shares, or exposure to the US stock market with an ETF like Vanguard S&P 500 ETF.
Additionally, ETFs can also be built to give exposure to specific regions, countries or economies. Examples of ETFs that are diversified across geographies include iShares MSCI Japan ETF, KraneShares CSI China Internet ETF, and JPMorgan BetaBuilders Europe ETF.
You can even gain exposure to specific industries and market niches, giving you access to sectors where purchasing and selling individual securities could pose challenges.
2. Cost effective [3]
ETFs offer multiple cost-saving advantages. For example, if you were to individually purchase all 500 stocks from the S&P 500, you’d incur fees for each trade, which easily adds up to a hefty cost and will eat into your potential earnings.
However, with ETFs, you can purchase an ETF like the SPY or that tracks the performance of all S&P500 stocks, in a single transaction with a single fee. This greatly lowers the overall expense of creating a diverse investment collection.
3. Transparency [4]
ETFs provide daily updates on their holdings, allowing investors to have a clear view of the specific assets held within the ETF. This transparency can be particularly beneficial for investors and traders who are looking for in-depth information about what they are investing in.
Here is an example:
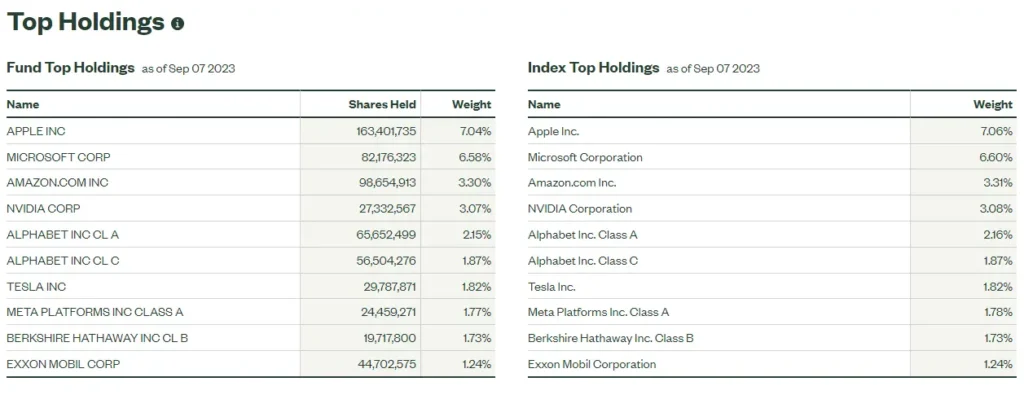
In the image above, traders will be able to see that the SPY ETF contains higher weightage in stocks like AAPL and MSFT, which is closely similar to the weightage those stocks have in the index SPY ETF is aiming to track.
4. Global exposure
With ETFs, you can trade and invest in a diverse range of assets from different countries and regions.
This global exposure helps spread risk and allows you to participate in the growth potential of international markets. It’s a straightforward way to expand your trading and investment opportunities beyond your local market, potentially increasing portfolio diversification and potential returns.
5. Receive dividends
When you trade ETFs, you have the advantage of receiving dividends from the assets within the ETF. This means you have the potential to earn a portion of the income generated from stocks or interest payments from bonds held by the ETF.
These dividends can provide a side stream of income, enhancing the overall return on your investment. It is a straightforward way to benefit from dividend payments without having to manage individual stocks in your portfolio.
What are the advantages of trading different types of ETFs?
Gold ETF [6]
Trading gold ETFs offers simple and convenient access to gold trading. Imagine buying a small piece of gold without needing to store it physically.
Gold ETFs track the price of gold (or gold mining companies), so when gold’s value goes up, the value of your ETF will rise in tandem. These ETFs are traded on the stock market, making buying and selling as easy as trading shares of a listed company. Gold ETFs also provide diversification – a way to spread risk by investing in a variety of gold-related assets. Plus, they can be more affordable than buying real gold.
In short, Gold ETFs provide a straightforward and cost-effective way to potentially benefit from the value of gold, all without the hassle of owning physical gold.
Bonds ETF [7]
A bond ETF consists of a basket of fixed income securities, also known as bonds. Bonds are loans issued by governments or corporations, issued to keen investors in return for periodic interest payments and repayment of the principal amount upon bond maturity.
The advantage of a bond ETF is its convenience in investing in multiple bonds without buying each one separately. This allows you to spread your money across multiple bonds, reducing the risk which comes in the form of companies defaulting and failing to repay the principal.
Also, bond ETFs are traded on stock exchanges, making them easy to buy and sell like stocks. They offer flexibility, liquidity, and usually have lower fees compared to traditional bond mutual funds. In summary, bond ETFs allow you to potentially earn periodic interest while also being more flexible and diverse than dealing with individual bonds.
Sector-specific ETF [8]
Sector-specific ETFs bundle stocks from specific industries, like grouping tech or healthcare companies. Imagine being able to ride on the newest trends, like trading an ETF that consists of companies within the electric vehicle (EV) space.
Sector-specific ETFs help to reduce risk by having various firms in that field, within a single ETF. They’re traded like stocks, easy to buy/sell, and can be cheaper than owning the stocks of an individual company. This helps you to spread your eggs in multiple baskets without having to pick stocks.
But remember, while they can bring gains, they remain exposed to the ups and downs of that industry. It’s like riding a tech wave – thrilling if it rises but complete with twists and turns.
Commodities ETF [9]
Commodities ETFs are one way for traders to trade different markets like precious metals, energy, agriculture, and more, allowing traders to gain exposure without directly owning physical goods.
For example, you can trade ETFs such as:
- iShares S&P GSCI Commodity-Indexed Trust
- SPDR S&P Oil and Gas Exploration and Production
- VanEck Oil Services ETF
Commodities ETF move in the opposite direction of stocks and bonds. This means that when stocks and bonds go down in value, commodities tend to go up, and vice versa. This can help traders spread out their holdings and not put all eggs in one basket.
Currency ETF [10, 11]
A currency ETF is an investment that mirrors the performance of a single currency or a basket of currencies. It enables regular individuals to participate in the forex market using a managed fund without placing individual trades.
Currency ETFs offer diversification, allowing investors and trades to mitigate risk associated with a single currency’s fluctuations. They provide transparency and liquidity, as they trade on major exchanges like stocks. Currency ETFs also allow traders to understand the international currency markets and hypothesis on currency movements.
Country/Region-based ETF [12]
Country ETFs are investment funds that track the performance of a specific country’s financial markets. Traders and investors can engage in specific countries and asset classes in alignment with their perspectives.
For example, if a trader has a strong belief in the potential expansion of the Indian market and aims to access Indian equities, they can trade an ETF that focuses on Indian equities, such as iShares MSCI India ETF. They have a more tax-efficient approach compared to trading in passive open or closed-end investment funds that focus on specific countries.
Read more about the different types of ETFs.
Key Takeaways for Benefits of ETFs Trading
ETFs offer diversification, liquidity, affordability, ease of trading, and tracking of various assets suitable for different trading goals. Intrigued by the benefits of trading ETFs? You can now trade ETFs CFDs with Vantage and experience a seamless trading journey!
Open a live account today to access a world of diversified trading opportunities and real-time market insights – start your ETFs CFDs trading experience with Vantage now.
References
- “What Is an ETF and How Does ETF CFD Trading Work? – FX Open” https://fxopen.com/blog/en/what-is-an-etf-and-how-does-etf-cfd-trading-work/ Accessed 8 August 2023
- “Benefits and considerations of ETFs – Schwab” https://www.schwab.com/etfs/benefits Accessed 8 August 2023
- “5 benefits of ETFs for investors – trackinsight” https://www.trackinsight.com/en/education/5-benefits-etfs-investors Accessed 9 August 2023
- “Advantages of ETFs – BlackRock” https://www.blackrock.com/hk/en/ishares/education/advantages-of-etfs Accessed 9 August 2023
- “Benefits of ETFs – Pros & Cons in Investment Portfolio – SoFi” https://www.sofi.com/learn/content/benefits-of-ETFs/ Accessed 9 August 2023
- “Everything You Need to Know About Gold ETFs – Money”. https://money.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-gold-etfs/ Accessed 10 August 2023
- “What Is a Bond ETF? Definition, Types, Examples, and How to Invest – Investopedia” https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/bond-etf.asp Accessed 10 August 2023
- “What is a Sector ETF, How Do You Invest in One? – Investopedia” https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/sector-etf.asp Accessed 10 August 2023
- “Investing in Commodity ETFs – Investopedia” https://www.investopedia.com/investing-commodity-etfs-4690946 Accessed 11 August 2023
- “Currency ETF: Meaning, Special Considerations, Examples – Investopedia” https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/currency-etf.asp#:~:text=Key%20Takeaways,burdens%20of%20placing%20individual%20trades Accessed 10 August 2023
- “Currency ETFs: Benefits, Risks, and Examples – Nasdaq” https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/currency-etfs-benefits-risks-and-examples – Accessed 10 August 2023
- “An introduction to Country-Based ETFs – ETF Central” https://www.etfcentral.com/news/introduction-country-based-etfs – Accessed 11 August 2023



