When trading the financial markets, it is essential to understand lot size, pips, and risk-to-reward ratio. This article explains what these terms mean and how to calculate them to become a more well-rounded trader.
What is Lot Size in Forex?
The term “Lot” will often appear in the vocabulary of traders, and it refers to the size of a trade. More specifically, a “Lot” in forex trading is the amount of currency units bought or sold in a trade.
Lot sizing plays an immense role in risk management. The differences in lot sizes fall into 4 categories: standard, mini, micro, and nano [1].
| Lots | Units | |
| Standard | 1 Lot | 100,000 |
| Mini | 0.1 Lot | 10,000 |
| Micro | 0.01 Lot | 1000 |
| Nano | 0.001 Lot | 100 |
Read all about micro lots and lot sizes here.
Using EURUSD as an example, when traders purchase 1 standard lot of EURUSD, it equates to buying 100,000 units of the base currency (EUR). If the price of EURUSD is 1.2000 (1 Euro = 1.2 USD), and a trader purchases 1 lot, it equates to the purchase of $100,000 Euros for $120,000 US Dollars.
Mini, micro, and nano lots are smaller divisions of the standard lot. The reason traders use a smaller lot size for trading is to attempt minimising risk to avoid big losses. A mini lot and micro lot accounts for 10% and 1% of a standard lot respectively. While a nano lot is not as common and only offered by selective brokers.
What Are Pips?
A “pip” is the unit of increment in a forex currency pair and is an acronym for percentage in point. Most forex currency pairs are up to four decimal places long and a pip is in the fourth decimal place.

However, do note that the pip for forex pairs with the Japanese Yen in them are usually at the second decimal place instead of the fourth. The reason Yen has a unique exception to the fourth decimal place rule is because 1 Japanese Yen is worth 1/100 of the US Dollar.
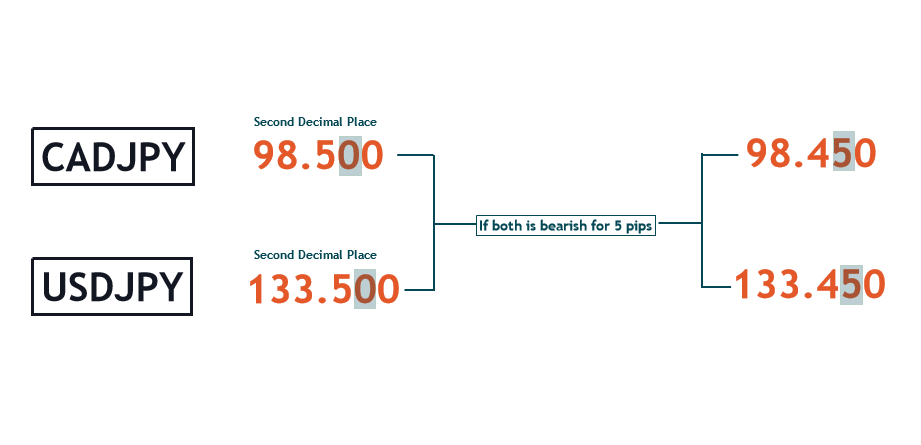
Combining Your Understanding of Lot Sizes, With Pips
A rule of thumb: For every standard lot opened, a one pip movement is worth $10.
In the same vein, a one pip movement on a mini lot is worth $1, and $0.10 on a micro lot.

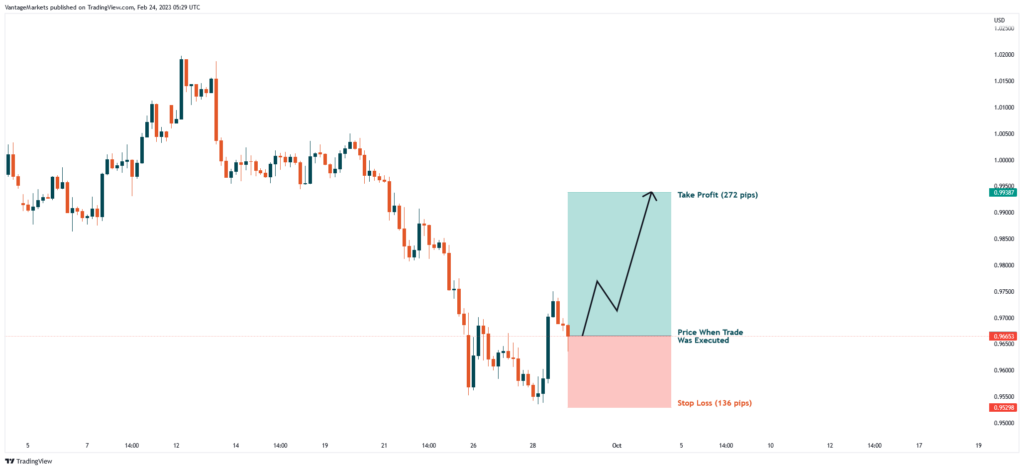
Using the EURUSD example from figure 4, if a trader follows the above idea and opens a 1 lot buy position, the expected loss would be $1360 (136 pips X $10/lot) and the expected profit would be $2720 (272 pips X $10/lot).
What is Risk-To-Reward Ratio?
The risk-to-reward ratio is used by traders to calculate the expected profit of a forex pair against the expected loss. This risk management tactic is implemented by seasoned traders to analyse investment opportunities and is said to be a key factor in trading success.
To find out what a trade’s risk-to-reward ratio is, simply divide the expected return, over the expected loss.
Figure 4 shows EURUSD on the H4 chart. If one were to plan a buy trade idea, the entry price, the expected loss price (stop loss), and the expected profit price (take profit) should be pre-planned beforehand. In the above example, the stop loss price from the entry price is 136 pips, while the take profit price from the entry is 272 pips. Dividing the take profit from the stop loss generates a risk/reward ratio of 1:2.
Although it may seem that the higher the risk-to-reward ratio, the more profits there is to be made. However, setting unrealistic risk-to-reward targets such as 1:20 may not be practical. It is important to be realistic about the risk-to-reward ratio so that trade analysis can be executed without emotions coming into play.
Conclusion
Understanding the key concepts of lot sizing, pip calculation, and risk-to-reward ratio is key to building the foundation of becoming a successful forex trader. Looking to apply these new concepts into trading CFDs? Open a demo account with Vantage and start trading, or head straight to the live markets.

References
- admintwfr2014. (2022, October 14). What is Lot Size in Forex? The World Financial Review. Retrieved December 29, 2022, from https://worldfinancialreview.com/what-is-lot-size-in-forex/.




