What is AUD/USD Trading?
The Australian Dollar is the fifth-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market and accounts for just under 7% of global FX turnover, according to the Bank of International Settlements.
Indeed, over 8% of Australia’s GDP is represented by the mining sector, while agricultural exports make up an additional 2%. With the majority of these exports being purchased by China, the performance of the world’s second-largest economy, and Australia’s largest trade partner, is also a key driver of the local currency and AUD/USD exchange rate in particular.
The “Aussie”, the colloquial name for the AUD/USD exchange rate, also exhibits a strong relationship with global equity markets and tends to perform better in an environment in which stock prices are rising. This sensitivity to benchmark stock market indices makes AUD/USD a great gauge of overall market sentiment.
Key Points
- The AUD/USD currency pair is influenced by global commodity prices, China’s economy, and central bank policies, reflecting Australia’s significant export-driven economic activity.
- Historical fluctuations in the AUD/USD exchange rate, such as its rise during China’s industrial expansion, illustrate its responsiveness to global economic shifts and commodity market trends.
- Traders are attracted to the AUD/USD pair for its high liquidity, clear technical patterns, and the potential for profit from volatility and economic indicators, with optimal trading times during overlapping market sessions.
AUD/USD History
Introduction of the Australian Dollar in 1966
The AUD/USD pair, one of the most traded globally, has a rich history starting with the introduction of the Australian Dollar (AUD) in 1966.
The AUD was originally pegged to the Great Britain Pound Sterling until 1967 when the Pound Sterling was devalued against the US Dollar.
However, the Australian Dollar chose to retain its peg to the US Dollar until 1971.
Introduction of Commodity Currency
As a commodity currency, the AUD’s value is significantly influenced by Australia’s export of resources like coal, gold, natural gas, and iron ore. Its performance is tied to global commodity prices, making it sensitive to global economic conditions and market sentiment.
For instance:
In the early 2010s, driven by China’s industrial boom, iron ore prices surged, reaching a peak of $180 per tonne [1]. As a reflection of this trend, the Australian Dollar (AUD) soared, at one point trading at 1.10 against the US Dollar (USD) in 2011, its highest level since the currency was floated in 1983 [2].
Major Historical Events — Float of AUD 1983
The Australian Dollar’s relationship with its US counterpart came into its own when the Australian Government floated the local currency in 1983. This meant that the value of the Australian Dollar would be set in the foreign exchange marketplace instead of maintained at a particular target price by the government.
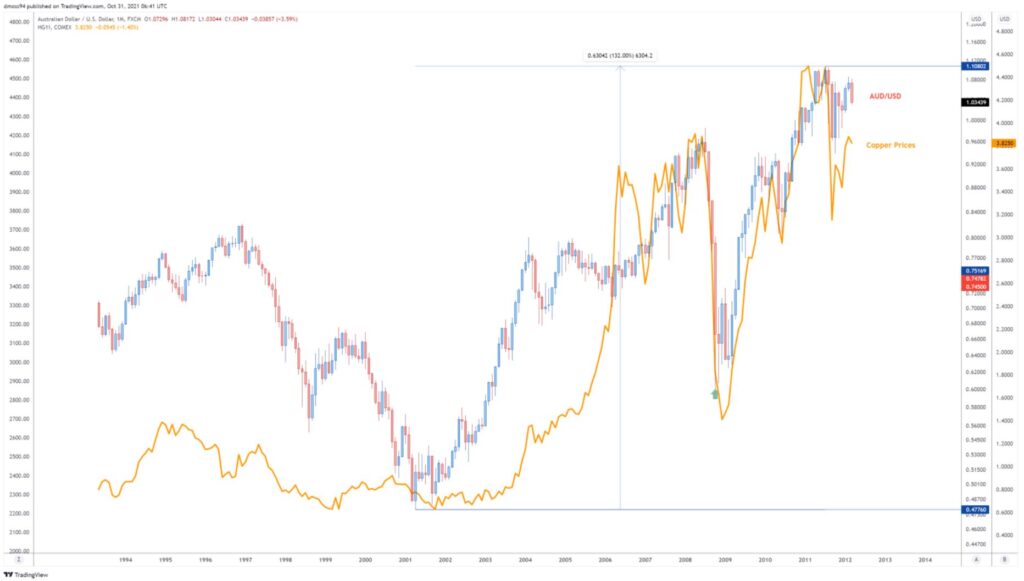
Since becoming a free-floating exchange rate, AUD/USD has fallen to a record low of 0.4775 in early 2001 before recovering over the next decade to set its record high of 1.1080 in 2011. Interestingly, this stratospheric run higher by the Aussie shows a strong positive correlation with the decade-long bull run seen in commodity markets.
Pictured below is AUD/USD’s meteoric climb between 2001 and 2011, with the price of copper overlayed.
Relationships with USD
The AUD/USD value is influenced by factors like interest rate differentials, economic indicators, and global risk sentiment. For example, when the Bank of Australia raises interest rates, it attracts foreign capital, leading to AUD appreciation against the USD. Conversely, during times of market uncertainty, traders may seek the safety of the USD, leading to a stronger USD and a weaker AUD.
Why Trade AUD/USD Currency Pair?
The AUD/USD currency pair is popular among traders due to its high liquidity and clear technical patterns.
As one of the major pairs in the forex market, it offers low spreads, reducing trading costs. The AUD, being a commodity currency, has a strong correlation with commodity prices, particularly gold and iron ore. This relationship provides unique trading opportunities based on commodity price movements.
Furthermore, the economic indicators and interest rate differentials between Australia and the U.S. often lead to predictable effects on this currency pair. This makes it easier for traders to develop strategies. The AUD/USD pair is also known for its volatility, which, while posing a risk, can also offer potential high returns for traders.
Historical Trends of AUD/USD Market [3]
- 2008
The year 2008 was marked by the global financial crisis, which had a significant impact on the AUD/USD exchange rate. The Australian Dollar (AUD) started the year at 0.88 USD but fell to 0.71 USD by the end of the year. This represented a decrease of 19.23%, reflecting the economic uncertainty and risk aversion during this period.
- 2010
In contrast to 2008, 2010 was a year of recovery for the AUD. It started the year at 0.91 USD and ended at 1.02 USD, an increase of 14.00%. This was due to the rebound in commodity prices and Australia’s strong economic performance, which boosted investor confidence in the AUD.
- 2022
The year 2022 saw a decrease in the value of the AUD against the USD. The AUD started the year at 0.73 USD and ended at 0.68 USD, a decrease of 6.38%. This was due to a combination of factors including the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and changes in monetary policy.
AUD/USD Prediction
Looking ahead, there are varying predictions for the AUD/USD exchange rate.
For instance, ANZ forecasts that the AUD will be worth 0.72 US cents by the end of 2025, while Westpac predicts 0.71, and NAB continues to aim high with a prediction of 0.75 US cents to 1 Australian dollar [4].
These predictions are based on factors such as economic growth, interest rates, and geopolitical events. However, it’s important to note that currency predictions are inherently uncertain and actual rates may vary.
What Moves the AUD/USD Exchange Rate?
Central Banks Decision
Central banks, specifically the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) and the US Federal Reserve (Fed) play a pivotal role in influencing the AUD/USD exchange rate. The decisions made by these institutions regarding monetary policy, such as interest rate changes and quantitative easing measures, have a direct impact on the value of the AUD and USD. Traders closely monitor central bank statements and meetings for clues about future policy direction.
Economic Indicators
Key economic indicators like GDP growth, employment figures, inflation rates, and manufacturing data provide crucial insights into the health and performance of the Australian and US economies.
Positive economic data in Australia typically strengthens the AUD, while strong data in the US bolsters the USD, affecting the AUD/USD exchange rate.
Visit the Vantage market news and analysis page to get all the latest market analysis, news and events.
Chinese Economy
China is Australia’s largest trading partner, and as such, the health of the Chinese economy has a significant impact on the AUD/USD pair. Changes in Chinese economic data, trade relations, and policies can influence Australian exports, and consequently, the AUD’s value. Economic events in China, such as shifts in growth rates or trade disputes, can create volatility in the AUD/USD exchange rate.
Interest Rate Differences
Interest rate differentials between Australia and the United States are a critical factor in AUD/USD movements. When the RBA raises interest rates or signals a more hawkish stance, it can attract foreign investment into Australian assets, leading to AUD appreciation. Conversely, when the Fed raises rates or adopts a more hawkish policy, it can strengthen the USD and weaken the AUD.
Commodity Prices
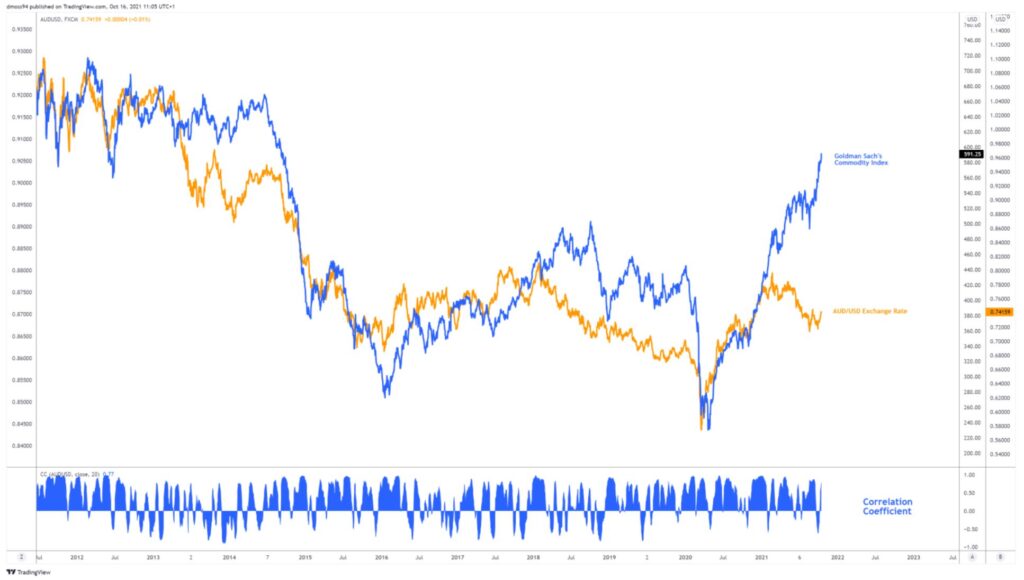
Given the Australian economy is a large exporter of several key commodities, such as copper, natural gas and iron ore, it is hardly surprising that the local currency’s trajectory is heavily influenced by the price trends of commodities. This relationship is highlighted below, with a strong positive correlation seen between AUD/USD and Goldman Sach’s commodity index. It is important to understand the overarching sentiment driving commodity markets, to identify the potential long-term trajectory of the Aussie.
AUD/USD Correlations
Positive Correlations [5,6]
Gold
The AUD/USD pair has a strong positive correlation with gold prices. This is because Australia is one of the world’s largest gold producers, and changes in gold prices can significantly impact the Australian economy and, consequently, the value of the AUD.
NZD/USD
The AUD/USD pair is highly correlated with the NZD/USD pair. This is because both Australia and New Zealand have similar economic structures and are heavily reliant on commodity exports.
EUR/USD
The AUD/USD pair also shows a positive correlation with the EUR/USD pair. This is because both pairs are quoted in US dollars, and any significant changes in the value of the USD can impact both pairs in the same way.
Negative Correlations [6,7]
USD/CAD
The AUD/USD pair has a negative correlation with the USD/CAD pair. This is because the CAD is also a commodity currency, and changes in commodity prices can have opposite effects on the AUD and CAD.
USD/JPY
The AUD/USD pair is negatively correlated with the USD/JPY pair. This is because the JPY is often considered a safe-haven currency and tends to strengthen during times of market uncertainty, which can lead to a weaker AUD.
USD/CHF
The AUD/USD pair also shows a negative correlation with the USD/CHF pair. This is because the CHF, like the JPY, is considered a safe-haven currency, and its value often increases during times of market volatility, leading to a weaker AUD.
How to Trade AUD/USD
In this section, we will delve into ways you can trade the AUD/USD currency pair, providing you with a comprehensive guide to navigate this popular forex market.
Trade AUD/USD Using Fundamental Analysis
A range of underlying fundamental variables influence the risk-sensitive AUD/USD exchange rate’s daily gyrations and ought to be constantly monitored when trading this forex pair.
Central Bank Policy and Interest Rate Differentials
The respective monetary policy settings of the US Federal Reserve and the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) can impact the trajectory of AUD/USD, through the influence each central bank has on interest rates.
As shown in the chart below, the local exchange rate exhibits a strong positive correlation with the interest rate differential between Australian 10-year Government Bonds and US 10-year Treasuries. This spread would widen when the RBA raises interest rates while the Federal Reserve keeps their respective policy settings stable, ultimately resulting in a positive inflow of capital to Australia and in turn strengthening the AUD/USD rate. The reverse is also true, with a hawkish shift in Fed policy likely narrowing this spread and undermining AUD/USD.
US 10-Year Treasury, Australian 10-Year Government Bond Spread Differential vs AUD/USD Exchange Rate

Local and Chinese Economic Data
With China accounting for over 42% of Australian exports, the overall performance of the world’s second-largest economy has a profound effect on AUD/USD. Generally, strong economic data out of China is supportive of the exchange rate, as it suggests strong demand for Australian exports. On the other hand, weak growth figures can significantly undermine AUD/USD, as market participants price less Chinese demand for Australian goods. Key economic data prints to keep an eye on are GDP, CPI, PPI, industrial output and major PMI releases.
US Equity Markets
As noted by the Reserve Bank of Australia, “the value of the Australian dollar tracks movements in other financial markets and changes in risk-sentiment (how much risk investors are willing to take on in their investments).
For example, if market participants are bullish on the outlook for economic growth they will be more prepared to take on more risk, which often coincides with an increased demand for Australian Dollars. Therefore, you tend to see the Australian dollar appreciate when global equity markets move higher and depreciate when equity markets fall.
The forex market reacts swiftly and often with high volatility to unexpected news or data releases. Being well-informed in real-time allows traders to assess risks, seize opportunities, and adjust strategies promptly. This ensures timely and well-informed decisions to navigate the ever-changing forex landscape successfully.
Stay up to date and gain access to real-time data by regularly checking Vantage’s economic calendar and sentiment indicators.
Trade AUD/USD Using Technical Analysis
Due to its popularity and high volume of market participation, AUD/USD tends to adhere to major psychological chart barriers and is also a prime candidate for breakout traders due to its aggressive moves out of consolidation patterns.
Price action trading
Support and resistance: When trading AUD/USD, horizontal support and resistance levels are pivotal when looking to execute a long or short trade on AUD/USD, with rates showing a tendency to retest former levels upon breakouts before establishing a new trend.
As seen in the chart below, key trend breaks often result in a short-term pullback before prices continue to accelerate aggressively in the direction of the original breakout.

Fibonacci: Fibonacci retracements are a quick and easy way of predicting support and resistance levels in Forex. They are based on the Fibonacci sequence, a mathematical concept where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones.
The most commonly used Fibonacci retracements levels are 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%. These levels represent potential points at which a currency pair may reverse its current trend. The Fibonacci tool works on the principle that markets tend to ‘retrace’ a portion of a move prior to continuing the dominant trend.
Indicator Trading
Indicator trading involves using various mathematical calculations and graphical representations to analyse historical price data. These indicators are designed to provide insights into market trends, momentum, volatility, and potential reversal points. Traders use them to identify buy and sell signals, confirm trends, and manage risk. Let’s look at two examples: Moving Averages and RSI.
Moving Averages: Moving averages are one of the simplest and most widely used forex indicators. They smooth out price data by calculating the average price over a specified period, helping traders identify trends and potential trend reversals.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI measures the speed and change of price movements. It ranges from 0 to 100 and is often used to identify overbought and oversold conditions. Traders look for RSI divergences and crossovers to make trading decisions.
Read our guide to technical indicators to help you understand the different types.
Risk Management
Risk management is crucial in AUD/USD trading due to forex market volatility. Key strategies include setting stop-loss and take-profit levels, diversifying the portfolio, and staying updated with economic news. These measures can help in potentially making returns while minimising losses.
AUD/USD Trading Strategies
Before going into individual strategies, let’s talk about what it means to go long and go short on AUD/USD.
What it means to short AUD/USD
Shorting the AUD/USD pair means that a trader believes the Australian dollar will depreciate against the US dollar.
In this scenario, the trader would sell AUD in the hope that its value will decrease. If the AUD does indeed fall in value relative to the USD, the trader can then buy back the AUD at a lower price, making a profit from the difference.
What it means to long AUD/USD
Going long on the AUD/USD pair means that a trader believes the Australian dollar will appreciate against the US dollar.
In this case, the trader would buy AUD in the expectation that its value will increase. If the AUD does rise in value relative to the USD, the trader can then sell the AUD at a higher price, thereby making a profit from the difference.
Here are some popular forex trading strategies you can use when trading AUD/USD.
Day Trading
Day trading involves speculating on securities by buying and selling them within the same trading day. Traders capitalise on short-term price fluctuations in various financial instruments such as stocks, options, and futures.
Day traders usually close all positions before the market closes to mitigate risks and prevent potential losses due to price gaps between the closing and opening prices of consecutive trading days.
Learn all about the difference between day trading and long term trading with our comprehensive article.
Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term investment strategy that involves taking positions in financial markets with the intention of holding them for an extended period, often months or even years.
Position traders base their decisions on fundamental analysis, which looks at factors like macroeconomic trends, company financials, and geopolitical circumstances to identify assets with long-term growth potential. They aim to benefit from major trends and market cycles, seeking substantial price movements over time.
Swing Trading
Swing trading focuses on capturing shorter- to medium-term price swings in the financial markets. Swing traders typically hold their positions for a few days to a few weeks, aiming to make gains from price changes during this time. They use tools like chart patterns and indicators to spot potential entry and exit points.
Swing trading strikes a balance between the quick pace of day trading and the long-term perspective of buy-and-hold investing, making it suitable for traders with other commitments who want to benefit from market ups and downs.
Read our article covering position trading vs swing trading to help you determine which can be more useful for your trading scenario.
Sentiment Trading
Sentiment trading, also known as sentiment analysis, involves assessing investor attitudes towards a market or asset. This method goes beyond traditional data points, incorporating emotions like fear and greed to gauge sentiment accurately.
Traders use tools like the VIX and Fear and Greed Index to understand market sentiment and make informed decisions. However, as human emotions can be unpredictable, sentiment analysis is best used alongside other strategies for optimal trading outcomes.
News Trading
News trading takes advantage of short-term price movements in financial markets following significant economic or geopolitical news releases. Traders keep an eye on economic calendars for scheduled data releases (like employment reports or interest rate decisions) and unexpected news (like geopolitical events or corporate earnings reports).
The goal is to swiftly assess how these events affect asset prices and make trades to profit from the resulting market fluctuations.
Best Time to Trade AUD/USD [8]
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across various trading sessions globally. For the AUD/USD pair, certain times are more volatile and hence potentially more profitable for traders. Understanding these market dynamics can help traders make informed decisions when navigating the forex market.
Overlapping Sessions
The most volatile periods for AUD/USD trading are during the overlapping sessions when both Australian and US markets are open.
These periods usually experience the highest liquidity and volatility, providing the best trading opportunities.
- Sydney and Tokyo (AEST 9:00 am – 12:00 pm): This period sees moderate volatility, suitable for traders who prefer a lower risk trading environment
- London and New York (EST 8:00 am – 12:00 pm): This period experiences high volatility, ideal for traders seeking significant price movements and short-term gains.
Asian Session Volatility
During the Asian trading session (AEST 7:00 am – 3:00 pm), the AUD/USD pair experiences moderate volatility.
This period is ideal for traders who prefer a less risky environment.
European and US Session Volatility
The AUD/USD pair’s volatility increases during the European and US sessions (EST 2:00 am – 4:00 pm), providing more trading opportunities but also higher risks.
Trading AUD/USD Currency Pair with Tight Spreads at Vantage
Open a position on major and minor currency pairs with competitive spreads on Vantage. Start trading AUD/USD with CFDs today!
You can open your live trading account in minutes at Vantage to start trading AUD/USD with CFDs. If you’re not ready to go live, open a free demo account to practice various trading strategies and techniques without having to deploy your own capital.
Get started with Vantage today!
FAQs for AUD/USD Trading
What is the Spread on AUD/USD at Vantage?
At Vantage, the spread on AUD/USD is competitively low. Traders can enjoy spreads starting from under 1 pip during high-liquidity periods. For RAW accounts, spreads start at 0.0 pip, and for Standard accounts, they start at 1.0 pip.
What are the risks of trading AUD/USD?
Trading AUD/USD comes with several risks:
- Economic Factors: Unexpected economic news or events, such as changes in interest rates, political instability, or natural disasters, can lead to significant price fluctuations.
- Commodity Dependency: Australia is a major exporter of commodities, such as iron ore, coal, and gold. Sudden fluctuations in commodity prices can impact the value of the Australian dollar.
- Currency Correlations: The AUD/USD pair is often influenced by the movements of other currency pairs, particularly those involving the US dollar.
Is AUD/USD a Good Pair to Trade?
AUD/USD can be a good pair to trade. It is one of the most traded currencies in the world, offering high liquidity, relatively attractive spreads, and a link to global economic trends. It often reacts swiftly to economic data and central bank policies, offering numerous trading opportunities.
When to Trade AUD/USD?
The best time to trade AUD/USD is possibly during the overlapping sessions when both Australian and US markets are open. This period usually experiences the highest liquidity and volatility, providing the best trading opportunities.
The most volatile periods are:
- Sydney and Tokyo (AEST 9:00 am – 12:00 pm): Moderate volatility, suitable for traders who prefer a lower risk trading environment.
- London and New York (EST 8:00 am – 12:00 pm): High volatility, ideal for traders seeking significant price movements and short-term gains.
References
- “Iron ore prices hit 3-month high – Financial Times” https://www.ft.com/content/8fff563c-cf3b-11e0-b6d4-00144feabdc0 Accessed 3 October 2023
- “Drivers of the Australian Dollar Exchange Rate – Reserve Bank of Australia” https://www.rba.gov.au/education/resources/explainers/drivers-of-the-aud-exchange-rate.html Accessed 3 October 2023
- “Australian – US Dollar Exchange Rate (AUD USD) – Historical Chart – macrotrends” https://www.macrotrends.net/2551/australian-us-dollar-exchange-rate-historical-chart Accessed 23 March 2024
- “AUD To USD Forecast: Will The Aussie Dollar Recover In 2024? – Forbes” https://www.forbes.com/advisor/au/investing/currencies/aud-to-usd-forecast-and-trends/ Accessed 23 March 2024
- “AUD/USD correlation explained – Forex Ratings” https://www.forex-ratings.com/forex-beginners/?id=31418 Accessed 23 March 2024
- “WHAT FOREX PAIRS ARE CORRELATED WITH AUD/USD? – Forex Academy” https://www.forex.academy/what-forex-pairs-are-correlated-with-audusd/ Accessed 23 March 2024
- “What Is AUDUSD and How Is It Related to Commodities? – Baxia” https://baxiamarkets.com/audusd-explained-and-relation-to-commodities/ Accessed 23 March 2024
- “Best Time to Trade AUD/USD – The Forex Geek” https://theforexgeek.com/best-time-to-trade-aud-usd/ Accessed 23 March 2024



